Collection: USS Belknap CG 26
The USS Belknap (CG-26) was a guided missile cruiser in the United States Navy, commissioned in 1975 and decommissioned in 1995. She was named for William J. Belknap, the 30th United States Secretary of War.
The Belknap was the first of her class of cruisers, and was designed to be the flagship of a destroyer flotilla. She was equipped with a variety of weapons systems, including the Tartar Guided Missile Fire Control System, the Mark 26 Guided Missile Launching System, and the Mark 92 Fire Control System.
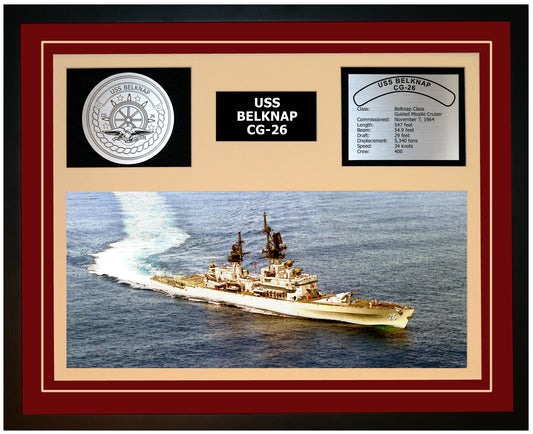
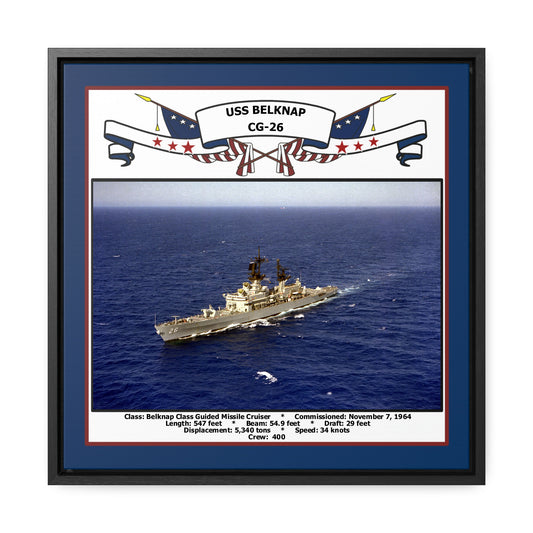
The Belknap had a length of 563 feet, a beam of 55 feet, and a draft of 31 feet. She had a displacement of 9,600 tons and was powered by four boilers and two geared turbines, giving her a maximum speed of 32 knots. She had a crew of 32 officers and 491 enlisted sailors.
The Belknap saw significant service during her 20-year career, including deployments to the Mediterranean Sea and the Persian Gulf. In 1980, she collided with the USS John F. Kennedy, causing significant damage to both ships. The incident was attributed to a communication breakdown and a lack of proper procedures for maneuvering in formation.
In 1983, the Belknap was part of the task force sent to Lebanon for peacekeeping operations during the Lebanese Civil War. She also participated in Operation Earnest Will, the escort of Kuwaiti oil tankers during the Iran-Iraq War.
The Belknap was decommissioned in 1995 and was struck from the Naval Vessel Register the following year. She was then transferred to the Maritime Administration for disposal.
Overall, the USS Belknap played a key role in the United States Navy's operations during the late 20th century, with her advanced weapons systems and capabilities making her an important asset in a number of conflicts and peacekeeping missions. Despite the tragic incident with USS John F. Kennedy, the ship and her crew served with distinction and honor throughout her time in service.
-
USS Belknap CG-26 Art Print
Regular price $ 59.99Regular priceUnit price / per$ 89.99Sale price $ 59.99Sale -
USS Belknap CG-26 Box Framed Canvas Art
Regular price $ 129.99Regular priceUnit price / per$ 169.99Sale price $ 129.99Sale -
USS Belknap CG-26 Canvas Photo Print
Regular price $ 49.99Regular priceUnit price / per$ 79.99Sale price $ 49.99Sale -
USS Belknap CG-26 Canvas Photo Print
Regular price $ 49.99Regular priceUnit price / per$ 79.99Sale price $ 49.99Sale -
USS Belknap CG-26 Coffee Cup Mug
Regular price From $ 24.99Regular priceUnit price / per$ 29.99Sale price From $ 24.99Sale -
USS BELKNAP CG-26 Framed Navy Ship Display
Regular price $ 239.99Regular priceUnit price / per$ 299.99Sale price $ 239.99Sale -
USS BELKNAP CG-26 Framed Navy Ship Photo 64CG26
Regular price $ 179.99Regular priceUnit price / per$ 199.99Sale price $ 179.99Sale -
USS BELKNAP CG-26 Framed Navy Ship Photo 65CG26
Regular price $ 179.99Regular priceUnit price / per$ 199.99Sale price $ 179.99Sale -
USS Belknap CG-26 Navy Floating Frame Photo
Regular price $ 129.99Regular priceUnit price / per$ 169.99Sale price $ 129.99Sale -
USS Belknap CG-26 Navy Floating Frame Photo
Regular price $ 129.99Regular priceUnit price / per$ 169.99Sale price $ 129.99Sale -
USS Belknap CG-26 Navy Ship Plaque
Regular price $ 59.99Regular priceUnit price / per$ 89.99Sale price $ 59.99Sale
-
United States Navy Honorable Engraved Discharge Certificate
Regular price $ 239.99Regular priceUnit price / per$ 229.99Sale price $ 239.99 -
Navy Veteran Oath of Enlistment
Regular price $ 239.99Regular priceUnit price / per$ 279.99Sale price $ 239.99Sale -
Navy Engraved Officer Oath of Office
Regular price $ 239.99Regular priceUnit price / per$ 279.99Sale price $ 239.99Sale